When it comes to managing and analyzing large amounts of data, traditional data warehouses have been the go-to solution for decades. But in recent years, a new challenger has emerged: Snowflake. So, what exactly is Snowflake, and how does it differ from traditional data warehouses?
To understand the differences, it’s important to first define what we mean by “traditional data warehouse.” Essentially, a traditional data warehouse is a large repository of structured data that’s been preprocessed, organized, and optimized for querying and analysis. Typically, data is loaded into the warehouse from a variety of sources, such as transactional databases, flat files, or external data feeds. The data is then transformed, cleaned, and loaded into the warehouse using ETL (extract, transform, load) processes.
Snowflake, on the other hand, is a cloud-based data warehouse that takes a different approach. Rather than requiring users to provision and manage their own hardware and software infrastructure, Snowflake is provided as a service. This means that all of the hardware, software, and networking is managed by Snowflake, allowing users to focus on analyzing their data rather than managing their infrastructure.
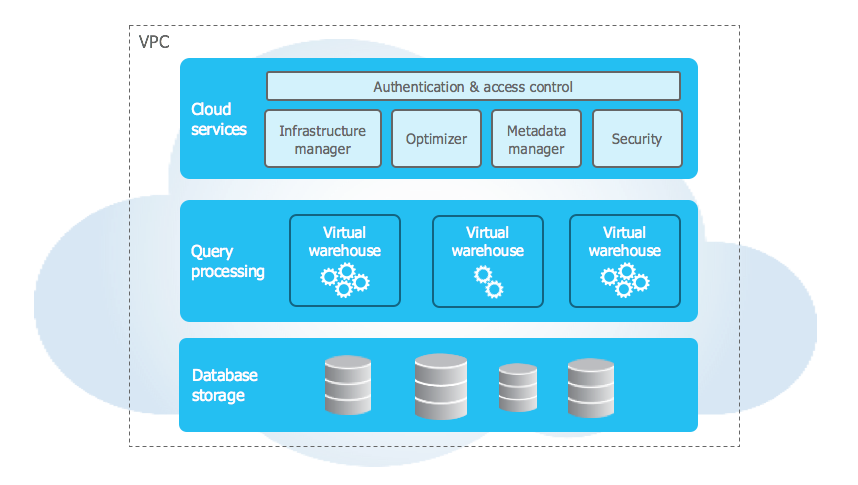
One of the key differences between Snowflake and traditional data warehouses is their architecture. Traditional data warehouses are typically implemented using a “shared-nothing” architecture, which means that data is partitioned and distributed across multiple nodes, each with its own CPU, memory, and storage. In contrast, Snowflake uses a hybrid of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing architectures. Snowflake stores all data in a central repository and accessed using a virtual warehouse. This allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as users can scale their virtual warehouse up or down depending on their needs, without worrying about the underlying hardware.
Another major difference is the pricing model. Traditional data warehouses typically require a significant upfront investment in hardware and software, and ongoing maintenance costs can be high. In contrast, Snowflake operates on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning that users only pay for the resources they use, without needing to invest in any upfront infrastructure. This can make it a more cost-effective option, particularly for smaller businesses that don’t have the resources to invest in a traditional data warehouse.
Finally, Snowflake offers a number of unique features that traditional data warehouses may not have. For example, Snowflake allows users to query data in real-time, using a combination of traditional SQL and advanced analytics techniques. Additionally, Snowflake offers built-in support for semi-structured data, such as JSON, XML, and Avro, making it easier to work with complex data types.
While traditional data warehouses have been the go-to solution for managing and analyzing large amounts of data for decades, Snowflake represents a new breed of cloud-based data warehouses that offer unique features, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re a small business just getting started with data analysis, or a large enterprise looking to modernize your data infrastructure, Snowflake is definitely worth considering as an alternative to traditional data warehouses.